-
1 gas insulated line
газоизолированная линия электропередачи
Линия электропередачи, токоведущие части которой заключены в металлический кожух, заполненный изолирующим газом.
[ ГОСТ 24291-90]EN
gas insulated line
gas insulated circuit (deprecated)
GIC (deprecated)
an electric line whose conductors are contained in a enclosure and insulated with a compressed gas
[IEV number 601-03-06]FR
ligne à isolation gazeuse
ligne électrique dont les conducteurs sont placés dans une enceinte et isolés par un gaz sous pression
NOTE – Le sigle CIG est à déconseiller.
[IEV number 601-03-06]Тематики
EN
DE
- Gassisolirte Leitung
- Leitung, gasisolierte
FR
53 газоизолированная линия электропередачи
Линия электропередачи, токоведущие части которой заключены в металлический кожух, заполненный изолирующим газом
601-03-06
de Gassisolirte Leitung
en gas insulated line
fr ligne à isolation gazeuse
Источник: ГОСТ 24291-90: Электрическая часть электростанции и электрической сети. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > gas insulated line
-
2 EMT
- электрический металлический кабелепровод
- тонкостенная металлическая труба для электропроводки
- встроенное устройство управления
встроенное устройство управления
Устройство, собирающее статистику и поддерживающее функции управления при установке в хост-модуль Token Ring. Примером такого устройства является Bay Networks Model 559.
[ http://www.lexikon.ru/dict/net/index.html]Тематики
EN
тонкостенная металлическая труба для электропроводки
-EN
electrical metallic tubing
A thin-walled metal raceway having a circular cross section; used to pull in or withdraw electric cables or wires after the tubing is installed in place; uses connectors and couplings other than the threaded type.
[ http://www.answers.com/topic/electrical-metallic-tubing-1]
intermediate metal conduit
IMC
-Intermediate metal conduit, or IMC for short, is a rigid steel electrical conduit that is lighter in weight than another rigid conduit. It was designed specifically to protect insulated electrical conductors and cables. It does the work of a similar conduit, galvanized rigid conduit (GRC), but with much less weight and thickness size. By utilizing IMC in areas allowed, you can all but eliminate the need for a heavier wall conduit.
IMC has other advantages over GRC. It has a larger interior diameter than Galvanized Rigid Conduit and the smoother interior of the pipe allows for easier wire pulling through the conduit.
IMC was originally introduced by Allied Tube & Conduit Corporation. It is manufactured in accordance with Underwriters’ Laboratories safety standard 1242 and ANSI C80.6. Believe it or not, Allied claims that IMC is actually more rigid than GRC in applications such as service masts and other installations. It has been installed in industrial and commercial buildings. In fact, the National Electrical Code has a specific article about IMC, article 342.
IMC conduit is coated in a hot galvanized coating on the exterior and a special corrosive-resistant coating on the inside to extend the conduit’s lifespan for reliability. Common conduit sizes range from ½” to 4”.
[ http://electrical.about.com/od/metalpvcconduit/a/IMCconduit.htm]Тематики
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
EN
электрический металлический кабелепровод
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > EMT
-
3 IMC
- тонкостенная металлическая труба для электропроводки
- регулятор с внутренней моделью
- международный центр технической эксплуатации
- Консорциум почты Internet
Консорциум почты Internet
См. www.imc.org.
[Л.М. Невдяев. Телекоммуникационные технологии. Англо-русский толковый словарь-справочник. Под редакцией Ю.М. Горностаева. Москва, 2002]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
EN
международный центр технической эксплуатации
—
[Л.Г.Суменко. Англо-русский словарь по информационным технологиям. М.: ГП ЦНИИС, 2003.]Тематики
EN
регулятор с внутренней моделью
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
тонкостенная металлическая труба для электропроводки
-EN
electrical metallic tubing
A thin-walled metal raceway having a circular cross section; used to pull in or withdraw electric cables or wires after the tubing is installed in place; uses connectors and couplings other than the threaded type.
[ http://www.answers.com/topic/electrical-metallic-tubing-1]
intermediate metal conduit
IMC
-Intermediate metal conduit, or IMC for short, is a rigid steel electrical conduit that is lighter in weight than another rigid conduit. It was designed specifically to protect insulated electrical conductors and cables. It does the work of a similar conduit, galvanized rigid conduit (GRC), but with much less weight and thickness size. By utilizing IMC in areas allowed, you can all but eliminate the need for a heavier wall conduit.
IMC has other advantages over GRC. It has a larger interior diameter than Galvanized Rigid Conduit and the smoother interior of the pipe allows for easier wire pulling through the conduit.
IMC was originally introduced by Allied Tube & Conduit Corporation. It is manufactured in accordance with Underwriters’ Laboratories safety standard 1242 and ANSI C80.6. Believe it or not, Allied claims that IMC is actually more rigid than GRC in applications such as service masts and other installations. It has been installed in industrial and commercial buildings. In fact, the National Electrical Code has a specific article about IMC, article 342.
IMC conduit is coated in a hot galvanized coating on the exterior and a special corrosive-resistant coating on the inside to extend the conduit’s lifespan for reliability. Common conduit sizes range from ½” to 4”.
[ http://electrical.about.com/od/metalpvcconduit/a/IMCconduit.htm]Тематики
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > IMC
-
4 intermediate metal conduit
- тонкостенная металлическая труба для электропроводки
- промежуточный металлический кабелепровод
- промежуточный металлический водовод
промежуточный металлический водовод
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
промежуточный металлический кабелепровод
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
тонкостенная металлическая труба для электропроводки
-EN
electrical metallic tubing
A thin-walled metal raceway having a circular cross section; used to pull in or withdraw electric cables or wires after the tubing is installed in place; uses connectors and couplings other than the threaded type.
[ http://www.answers.com/topic/electrical-metallic-tubing-1]
intermediate metal conduit
IMC
-Intermediate metal conduit, or IMC for short, is a rigid steel electrical conduit that is lighter in weight than another rigid conduit. It was designed specifically to protect insulated electrical conductors and cables. It does the work of a similar conduit, galvanized rigid conduit (GRC), but with much less weight and thickness size. By utilizing IMC in areas allowed, you can all but eliminate the need for a heavier wall conduit.
IMC has other advantages over GRC. It has a larger interior diameter than Galvanized Rigid Conduit and the smoother interior of the pipe allows for easier wire pulling through the conduit.
IMC was originally introduced by Allied Tube & Conduit Corporation. It is manufactured in accordance with Underwriters’ Laboratories safety standard 1242 and ANSI C80.6. Believe it or not, Allied claims that IMC is actually more rigid than GRC in applications such as service masts and other installations. It has been installed in industrial and commercial buildings. In fact, the National Electrical Code has a specific article about IMC, article 342.
IMC conduit is coated in a hot galvanized coating on the exterior and a special corrosive-resistant coating on the inside to extend the conduit’s lifespan for reliability. Common conduit sizes range from ½” to 4”.
[ http://electrical.about.com/od/metalpvcconduit/a/IMCconduit.htm]Тематики
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > intermediate metal conduit
-
5 electrical metallic tubing
- электрический металлический кабелепровод
- тонкостенная металлическая трубка для проводов
- тонкостенная металлическая труба для электропроводки
тонкостенная металлическая труба для электропроводки
-EN
electrical metallic tubing
A thin-walled metal raceway having a circular cross section; used to pull in or withdraw electric cables or wires after the tubing is installed in place; uses connectors and couplings other than the threaded type.
[ http://www.answers.com/topic/electrical-metallic-tubing-1]
intermediate metal conduit
IMC
-Intermediate metal conduit, or IMC for short, is a rigid steel electrical conduit that is lighter in weight than another rigid conduit. It was designed specifically to protect insulated electrical conductors and cables. It does the work of a similar conduit, galvanized rigid conduit (GRC), but with much less weight and thickness size. By utilizing IMC in areas allowed, you can all but eliminate the need for a heavier wall conduit.
IMC has other advantages over GRC. It has a larger interior diameter than Galvanized Rigid Conduit and the smoother interior of the pipe allows for easier wire pulling through the conduit.
IMC was originally introduced by Allied Tube & Conduit Corporation. It is manufactured in accordance with Underwriters’ Laboratories safety standard 1242 and ANSI C80.6. Believe it or not, Allied claims that IMC is actually more rigid than GRC in applications such as service masts and other installations. It has been installed in industrial and commercial buildings. In fact, the National Electrical Code has a specific article about IMC, article 342.
IMC conduit is coated in a hot galvanized coating on the exterior and a special corrosive-resistant coating on the inside to extend the conduit’s lifespan for reliability. Common conduit sizes range from ½” to 4”.
[ http://electrical.about.com/od/metalpvcconduit/a/IMCconduit.htm]Тематики
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
EN
тонкостенная металлическая трубка для проводов
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
электрический металлический кабелепровод
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > electrical metallic tubing
-
6 raceway
- труба для электропроводки
- система специальных кабельных коробов
- система кабельных коробов
- рабочая поверхность подшипника
- прямая секция кабельного короба
- канал для электропроводки
- кабельный канал
- кабелепровод
- водопроводный канал
кабелепровод
Любой канал, обеспечивающий прокладку кабелей, в том числе, металлические и пластмассовые трубопроводы, рукава, каналы в полах, сотовые фальшполы, сетчатые лотки, желоба и кабель каналы (ISO/IEC 11801).
[ http://www.iks-media.ru/glossary/index.html?glossid=2400324]
кабелепровод
трасса
кабельный канал
Трасса или структура, предназначенная или используемая для прокладки и монтажа телекоммуникационных кабелей.
[ http://www.lanmaster.ru/SKS/DOKUMENT/568b.htm]Тематики
- СКС (структурированные кабельные системы)
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
EN
кабельный канал
Кабельным каналом называется закрытое и заглубленное (частично или полностью) в грунт, пол, перекрытие и т. п. непроходное сооружение, предназначенное для размещения в нем кабелей, укладку, осмотр и ремонт которых возможно производить лишь при снятом перекрытии.
[ПУЭ. Раздел 2]
кабельный канал
Элемент системы электропроводки, расположенный над землей или полом или в земле или в полу, открытый, вентилируемый или замкнутый, размеры которого не позволяют вход людей, но обеспечивают доступ к трубам и (или) кабелям по всей длине в процессе монтажа и после него.
Примечание - Кабельный канал может составлять или не составлять часть конструкции здания
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
канал кабельный
Подземный непроходной канал, предназначенный для размещения электрических кабелей
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
cable channel
element of a wiring system above or in the ground or floor, open, ventilated or closed, and having dimensions which do not permit the entry of persons but allow access to the conduits and/or cables throughout their length during and after installation
NOTE – A cable channel may or may not form part of the building construction.
[IEV number 826-15-06]FR
caniveau, m
élément de canalisation situé au-dessus ou dans le sol ou le plancher, ouvert, ventilé ou fermé, ayant des dimensions ne permettant pas aux personnes d'y circuler, mais dans lequel les conduits ou câbles sont accessibles sur toute leur longueur, pendant et après installation
NOTE – Un caniveau peut ou non faire partie de la construction du bâtiment.
[IEV number 826-15-06]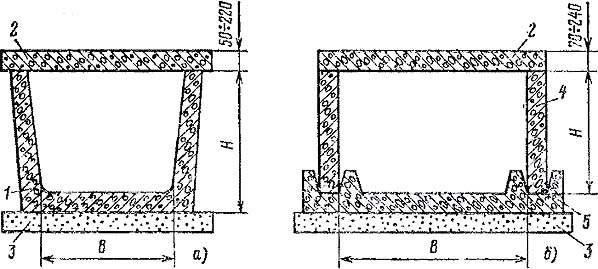
Кабельные каналы:
а — лотковый типа ЛК; б — из сборных плит типа СК:1 — лоток; 2 — плита перекрытия; 3 — подготовка; 4 — плита стеновая; 5 — основание
Высота кабельных каналов в свету не ограничивается, но бывает не более 1200 мм. Ширина каналов определяется в зависимости от размеров применяемых кабельных конструкций из условия сохранения прохода не менее 300 мм при глубине канала до 600 мм, 450 мм — от более 600 до 900 мм, 600 мм при более 900 мм.
Полы в каналах выполняют с уклоном не менее 0,5% в сторону водосборников или ливневой канализации.
Для крепления кабельных конструкций в стенах каналов через каждые 0,8—1 м (по длине) устанавливают закладные детали. При заводском изготовлении стеновых панелей детали устанавливают на предприятии-изготовителе. Закладные детали в каналах глубиной до 600 мм располагают в один ряд, при большей глубине каналов — в два ряда.
В местах поворота и разветвления трассы устраивают уширительные камеры, размеры которых выбирают с учетом допускаемого радиуса изгиба прокладываемого кабеля.
[ http://forca.ru/knigi/oborudovanie/priemka-zdaniy-i-sooruzheniy-pod-montazh-elektrooborudovaniya-11.html]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Примечание(1)- Мнение автора карточкиТематики
- кабели, провода...
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
- электроустановки
Обобщающие термины
EN
- cable channel
- cable duct
- cable trench
- cabling
- conduit
- duct
- electric raceway
- raceway
- trench for cabling
DE
FR
- caniveau du câble
- caniveau, m
- conduite du câble
канал для электропроводки
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
прямая секция кабельного короба
Основной компонент системы кабельных коробов, состоящий из основания (корпуса) со съемной или открывающейся крышкой
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61084-1 2007]
прямая секция
Для прямолинейных участков электропроводки без ответвлений и для прямолинейных участков электропроводки с устройствами для ответвлений одиночными кабелями
[ ГОСТ 20803-81]
прямая секция кабельного короба
-
[IEV number 442-02-37]EN
trunking length
the main component of a cable trunking system comprising a base with a removable cover
[IEV number 442-02-37]FR
(longueur de) goulotte
élément principal d'un système de goulottes constitué d'un fond avec un couvercle amovible
[IEV number 442-02-37]
Прямая секция кабельного короба
[ http://mks.montak.ru/catalog/182/232]Тематики
- изделие электромонтажное
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
EN
DE
FR
рабочая поверхность подшипника
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
система кабельных коробов
Система замкнутых оболочек, состоящих из основания (корпуса) и съемной крышки, предназначенная дляполного заключения в себяпрокладки внутри неё изолированных проводов, кабелей, шнуров и (или) для размещения другого электрического оборудования, включая оборудование информационных технологий.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
система кабельных коробов
Система замкнутых оболочек, состоящих из корпуса со съемной или открывающейся крышкой, предназначенная для прокладки внутри нее изолированных проводов, кабелей и шнуров и/или для размещения другого электрооборудования.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61084-1 2007]
кабельнесущая система
Система закрытых оболочек, допускающая размещение изолированных проводов на базе подвижных поверхностей и предназначенная для полной защиты изолированных проводов, кабелей, шнуров, а также для размещения другого электрооборудования.
система кабельных коробов
Система закрываемых полых конструкций, состоящая из основания (корпуса) и съемной крышки, предназначенная для прокладки внутри них и защиты от механических повреждений кабелей, шнуров, изолированных проводов и (или) для размещения другого электрического оборудования, включая оборудование информационных технологий.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]
Примечание. Синим цветом обозначен вариант, предлагаемый автором карточки.EN
cable trunking system
a system of closed enclosures comprising a base with a removable cover, intended for the complete surrounding of insulated conductors, cables, cords and/or for the accommodation of other electrical accessories
Source: 826-06-04 MOD
[IEV number 442-02-34]
cable trunking system
system of closed enclosures comprising a base with a removable cover, intended for the complete surrounding of insulated conductors, cables, cords and/or for the accommodation of other electric equipment including information technology equipment
Source: 442-02-34 MOD
[IEV number 826-15-04]
[IEC 60204-1-2006]FR
système de goulottes
ensemble d'enveloppes fermées munies d'un fond avec un couvercle amovible et destiné à la protection complète de conducteurs isolés et de câbles, ou au logement d'autre petit appareillage électrique
Source: 826-06-04 MOD
[IEV number 442-02-34]
système de goulottes, m
ensemble d'enveloppes fermées, munies d'un fond avec un couvercle amovible et destiné à la protection complète des conducteurs isolés et des câbles et/ou au logement d'autres matériels électriques y compris des matériels de traitement de l'information
Source: 442-02-34 MOD
[IEV number 826-15-04]Обратите внимание!
Различают два вида систем кабельных коробов:
1) (просто) система кабельных коробов (cable trunking system) - система любого сечения, но обязательно с крышкой;
2) система специальных кабельных коробов (cable ducting system) - система некруглого сечения и без крышек.
Примечание. В ПУЭ короб без крышки называется глухой короб (см. кабельный короб)
[Автор карточки]
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Raceways shall be one- or two-piece design with base and snap-on cover, or three-piece design with base and two snap-on covers which snap side by side on a common base.
[Legrand/Wiremold. SECTION 16130 RACEWAY AND BOXES]В состав поставки входят специальные (глухие) кабельные короба, а также кабельные короба, состоящие из основания и защелкивающейся крышки, или из основания и двух защелкивающихся крышек.
[Перевод Интент]
1 - Система кабельных коробов
Система кабельных коробов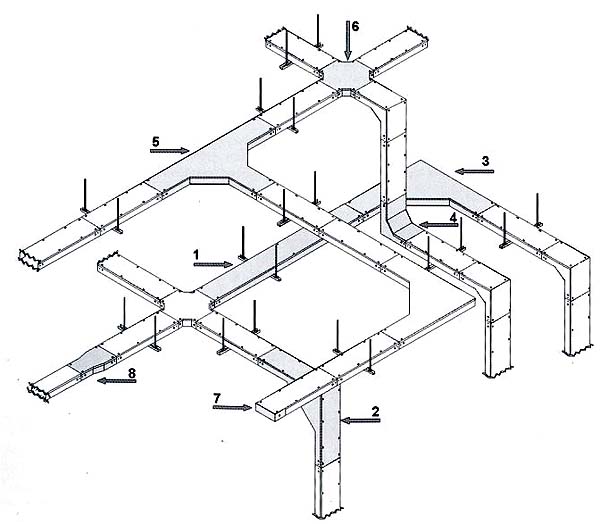
Система кабельных коробов
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Примечание(1) - мнение автора карточкиТематики
- изделие электромонтажное
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
EN
DE
FR
система специальных кабельных коробов
Система замкнутых оболочек некруглого сечения, не имеющая съемных или открывающихся крышек, предназначенная для прокладки изолированных проводов, кабелей и шнуров в электрических установках, допускающая их затяжку в нее и их замену
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
система специальных кабельных коробов
Система коробовпрямоугольногонекруглого сечения, не имеющих съемных или открывающихся крышек, предназначенная для прокладки внутри нее изолированных проводов и кабелей и обеспечивающая возможность затяжки в короба проводов и кабелей и их замены.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61084-1 2007]EN
cable ducting system
a system of closed enclosures of non-circular section, for insulated conductors, cables and cords in electrical installations, allowing them to be drawn in and replaced
[IEV number 442-02-35]FR
système de conduits profilés
ensemble d'enveloppes fermées, de section non circulaire, destiné à la mise en place ou au remplacement de conducteurs isolés ou de câbles, par tirage, dans des installations électriques
[IEV number 442-02-35]Обратите внимание!
Различают два вида систем кабельных коробов:
1) (просто) система кабельных коробов (cable trunking system) - система любого сечения, но обязательно с крышкой;
2) система специальных кабельных коробов (cable ducting system) - система некруглого сечения и без крышек.
[Интент]
Рис. Panduit®
Система специальных кабельных коробов
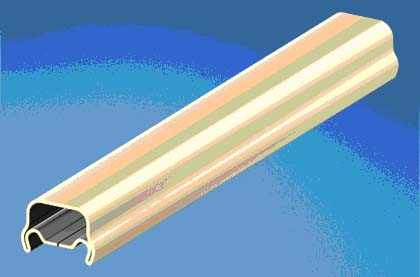
Рис. Panduit®
Прямая секция системы специальных кабельных коробовТематики
- изделие электромонтажное
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
EN
DE
- geschlossener Elektroinstallationskanal, m
FR
труба
Компонентзащищеннойтрубной электропроводки, имеющий, как правило, круглое поперечное сечение, предназначенный для прокладки изолированных проводов и(или) кабелей в электрических или коммуникационных установках, допускающий их затяжку в него и(или) их замену.
ПримечаниеСоединения труб должны быть достаточно плотными, чтобы изолированные провода и (или) кабели могли быть только затянуты, но не введены сбоку в просвет между трубами.
Трубы должны располагаться достаточно близко друг от друга, так чтобы отсутствовала возможность затянуть изолированные провода и (или) кабели в просвет между ними.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
трубопроводтруба
Закрытый элемент кабельной конструкцииКомпонент трубной электропроводки круглого или иного сечения для прокладки в электрических установках кабелей и/или изолированных проводови/или кабелей в электрических установках,позволяющий производить ихвыемкузатяжку и/или замену.
Примечание
Трубопроводы должны быть закрыты таким образом, чтобы имелась возможность вставлять в них изолированные провода и/или кабели.
Трубы должны располагаться достаточно близко друг от друга, так чтобы отсутствовала возможность затянуть изолированные провода и (или) кабели в просвет между ними.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]
Примечание. Синим цветом обозначен вариант, предлагаемый автором карточки.EN
conduit
a part of a closed wiring system of generally circular cross section for insulated conductors and/or cables in electrical or communication installations, allowing them to be drawn in and/or replaced
Source: 826-06-03 MOD
[IEV number 442-02-03]
conduit
part of a closed wiring system of circular or non-circular cross-section for insulated conductors and/or cables in electrical installations, allowing them to be drawn in and/or replaced
NOTE Conduits should be sufficiently close-jointed so that the insulated conductors and/or cables can only be drawn in and not inserted laterally.
[IEV 826-06-03]
[IEC 60204-1-2006]
raceway
A tube that encloses and protects electric wires.
[ http://www.answers.com/topic/raceway]FR
conduit
élément d'un système de canalisation fermé de section droite généralement circulaire, destiné à la mise en place par tirage ou au remplacement des conducteurs ou des câbles isolés dans les installations électriques ou de télécommunication
Source: 826-06-03 MOD
[IEV number 442-02-03]См. также пластмассовые трубы для электропроводок
См. также стальные трубы для электропроводок
4.1. Для прокладки проводов и кабелей необходимо применять специальные трубы для электропроводок: гладкие из непластифицированного ПВХ по ТУ 6-19-215-86, прил. 2; гладкие из вторичного ПЭ по ТУ 63.178-103-85, прил. 3; гладкие из наполненного ПЭ по ТУ 6-19-051-575-85, прил. 4; гофрированные из НПВХ по ТУ 6-19-051-419-84, прил. 5; гофрированные из ПЭ по ТУ 6-19-051-518-87, прил.6; гофрированные из вторичного ПЭ по ТУ 63.178-117-87, прил.7. При отсутствии указанных труб применяют технологические трубы: гладкие напорные из НПВХ по ТУ 6-19-231-87, прил.8; гладкие напорные из ПЭ низкого и высокого давления по ГОСТ 18599-83, прил. 9; гладкие из ПП по ТУ 38-102-100-76, прил. 10; трубы из вторичного ПЭ по ТУ 6-19-133-79, прил. П.
...
4.3. Применяют также трубы стальные электросварные по ГОСТ 10704-76 сортамент, прил. 12, легкие и обыкновенные водогазопроводные по ГОСТ 3262-75*, прил.13.[Министерство архитектуры, строительства и жилищно-коммунального хозяйства. Концерн «ЭЛЕКТРОМОНТАЖ». Инструкция по монтажу электропроводок в трубах]
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Примечание(1)- Мнение автора карточкиТематики
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > raceway
-
7 switchboard
- распределительный щит
- распределительное устройство
- НКУ распределения и управления
- коммутационный щит
- коммутаторная панель
- коммутатор
коммутатор
Устройство, обеспечивающее посредством включения, отключения и переключения электрических цепей выбор требуемой выходной цепи и соединение с ней входной цепи
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
EN
DE
FR
коммутаторная панель
распределительный щит
Устройство, конструктивно объединяющее несколько коммутационных элементов, предназначенных для включения, отключения и переключения электрических цепей и каналов связи в ручном режиме.
[Л.М. Невдяев. Телекоммуникационные технологии. Англо-русский толковый словарь-справочник. Под редакцией Ю.М. Горностаева. Москва, 2002]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
коммутационный щит
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
низковольтное устройство распределения и управления (НКУ)
Низковольтные коммутационные аппараты и устройства управления, измерения, сигнализации, защиты, регулирования, собранные совместно, со всеми внутренними электрическими и механическими соединениями и конструктивными элементами.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61439-1-2012]
низковольтное устройство распределения и управления
Комбинация низковольтных коммутационных аппаратов с устройствами управления, измерения, сигнализации, защиты, регулирования и т. п., полностью смонтированных изготовителем НКУ (под его ответственность на единой конструктивной основе) со всеми внутренними электрическими и механическими соединениями с соответствующими конструктивными элементами
Примечания
1. В настоящем стандарте сокращение НКУ используют для обозначения низковольтных комплектных устройств распределения и управления.
2. Аппараты, входящие в состав НКУ, могут быть электромеханическими или электронными.
3. По различным причинам, например по условиям транспортирования или изготовления, некоторые операции сборки могут быть выполнены на месте установки, вне предприятия-изготовителя.
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]EN
power switchgear and controlgear assembly (PSC-assembly)
low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly used to distribute and control energy for all types of loads, intended for industrial, commercial and similar applications where operation by ordinary persons is not intended
[IEC 61439-2, ed. 1.0 (2009-01)]
low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
combination of one or more low-voltage switching devices together with associated control, measuring, signalling, protective, regulation equipment, etc., completely assembled under the responsibility of the manufacturer with all the internal electrical and mechanical interconnections and structural parts.
[IEC 61892-3, ed. 2.0 (2007-11)]
switchgear and controlgear
a general term covering switching devices and their combination with associated control, measuring, protective and regulating equipment, also assemblies of such devices and equipment with associated interconnections, accessories, enclosures and supporting structures
[IEV number 441-11-01]
switchgear and controlgear
electric equipment intended to be connected to an electric circuit for the purpose of carrying out one or more of the following functions: protection, control, isolation, switching
NOTE – The French and English terms can be considered as equivalent in most cases. However, the French term has a broader meaning than the English term and includes for example connecting devices, plugs and socket-outlets, etc. In English, these latter devices are known as accessories.
[IEV number 826-16-03 ]
switchboard
A large single electric control panel, frame, or assembly of panels on which are mounted (either on the back or on the face, or both) switches, overcurrent and other protective devices, buses, and usually instruments; not intended for installation in a cabinet but may be completely enclosed in metal; usually is accessible from both the front and rear.
[ McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Architecture & Construction]
switchboard
One or more panels accommodating control switches, indicators, and other apparatus for operating electric circuits
[ The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language]FR
ensemble d'appareillage de puissance (ensemble PSC)
ensemble d'appareillage à basse tension utilisé pour répartir et commander l'énergie pour tous les types de charges et prévu pour des applications industrielles, commerciales et analogues dans lesquelles l'exploitation par des personnes ordinaires n'est pas prévue
[IEC 61439-2, ed. 1.0 (2009-01)]
appareillage, m
matériel électrique destiné à être relié à un circuit électrique en vue d'assurer une ou plusieurs des fonctions suivantes: protection, commande, sectionnement, connexion
NOTE – Les termes français et anglais peuvent être considérés comme équivalents dans la plupart des cas. Toutefois, le terme français couvre un domaine plus étendu que le terme anglais, et comprend notamment les dispositifs de connexion, les prises de courant, etc. En anglais, ces derniers sont dénommés "accessories".
[IEV number 826-16-03 ]
appareillage
terme général applicable aux appareils de connexion et à leur combinaison avec des appareils de commande, de mesure, de protection et de réglage qui leur sont associés, ainsi qu'aux ensembles de tels appareils avec les connexions, les accessoires, les enveloppes et les charpentes correspondantes
[IEV number 441-11-01]
A switchboard as defined in the National Electrical Code is a large single panel, frame, or assembly of panels on which are mounted, on the face or back or both switches, overcurrent and other protective devices, buses, and, usually, instruments.
Switchboards are generally accessible from the rear as well as from the front and are not intended to be installed in cabinets.
The types of switchboards, classified by basic features of construction, are as follows:
1. Live-front vertical panels
2. Dead-front boards
3. Safety enclosed boards( metal-clad)
[American electricians’ handbook]
The switchboard plays an essential role in the availability of electric power, while meeting the needs of personal and property safety.
Its definition, design and installation are based on precise rules; there is no place for improvisation.
The IEC 61439 standard aims to better define " low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies", ensuring that the specified performances are reached.
It specifies in particular:
> the responsibilities of each player, distinguishing those of the original equipment manufacturer - the organization that performed the original design and associated verification of an assembly in accordance with the standard, and of the assembly manufacturer - the organization taking responsibility for the finished assembly;
> the design and verification rules, constituting a benchmark for product certification.
All the component parts of the electrical switchboard are concerned by the IEC 61439 standard.
Equipment produced in accordance with the requirements of this switchboard standard ensures the safety and reliability of the installation.
A switchboard must comply with the requirements of standard IEC 61439-1 and 2 to guarantee the safety and reliability of the installation.
Managers of installations, fully aware of the professional and legal liabilities weighing on their company and on themselves, demand a high level of safety for the electrical installation.
What is more, the serious economic consequences of prolonged halts in production mean that the electrical switchboard must provide excellent continuity of service, whatever the operating conditions.
[Schneider Electric]НКУ играет главную роль в обеспечении электроэнергией, удовлетворяя при этом всем требованиям по безопасности людей и сохранности имущества.
Выбор конструкции, проектирование и монтаж основаны на чётких правилах, не допускающих никакой импровизации.
Требования к низковольтным комплектным устройствам распределения и управления сформулированы в стандарте МЭК 61439 (ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000).
В частности, он определяет:
> распределение ответственности между изготовителем НКУ - организацией, разработавшей конструкцию НКУ и проверившей его на соответствие требованиям стандарта, и сборщиком – организацией, выполнившей сборку НКУ;
> конструкцию, технические характеристики, виды и методы испытаний НКУ.
В стандарте МЭК 61439 (ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000) описываются все компоненты НКУ.
Оборудование, изготовленное в соответствии с требованиями этого стандарта, обеспечивает безопасность и надежность электроустановки.
Для того чтобы гарантировать безопасность эксплуатации и надежность работы электроустановки, распределительный щит должен соответствовать требованиям стандарта МЭК 61439-1 и 2.
Лица, ответственные за электроустановки, должны быть полностью осведомлены о профессиональной и юридической ответственности, возложенной на их компанию и на них лично, за обеспечение высокого уровня безопасности эксплуатации этих электроустановок.
Кроме того, поскольку длительные перерывы производства приводят к серьезным экономическим последствиям, электрический распределительный щит должен обеспечивать надежную и бесперебойную работу независимо от условий эксплуатации.
[Перевод Интент]LV switchgear assemblies are undoubtedly the components of the electric installation more subject to the direct intervention of personnel (operations, maintenance, etc.) and for this reason users demand from them higher and higher safety requirements.
The compliance of an assembly with the state of the art and therefore, presumptively, with the relevant technical Standard, cannot be based only on the fact that the components which constitute it comply with the state of the art and therefore, at least presumptively, with the relevant technical standards.
In other words, the whole assembly must be designed, built and tested in compliance with the state of the art.
Since the assemblies under consideration are low voltage equipment, their rated voltage shall not exceed 1000 Va.c. or 1500 Vd.c. As regards currents, neither upper nor lower limits are provided in the application field of this Standard.
The Standard IEC 60439-1 states the construction, safety and maintenance requirements for low voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies, without dealing with the functional aspects which remain a competence of the designer of the plant for which the assembly is intended.
[ABB]Низковольтные комплектные устройства (НКУ), вне всякого сомнения, являются частями электроустановок, которые наиболее подвержены непосредственному вмешательству оперативного, обслуживающего и т. п. персонала. Вот почему требования потребителей к безопасности НКУ становятся все выше и выше.
Соответствие НКУ современному положению дел и вследствие этого, гипотетически, соответствующим техническим стандартам, не может основываться только на том факте, что составляющие НКУ компоненты соответствуют современному состоянию дел и поэтому, по крайней мере, гипотетически, - соответствующим техническим стандартам
Другими словами, НКУ должно быть разработано, изготовлено и испытано в соответствии с современными требованиями.
Мы рассматриваем низковольтные комплектные устройства и это означает, что их номинальное напряжение не превышает 1000 В переменного тока или 1500 В постоянного тока. Что касается тока, то ни верхнее, ни нижнее значение стандартами, относящимися к данной области, не оговариваются
Стандарт МЭК 60439-1 устанавливает требования к конструкции, безопасности и техническому обслуживанию низковольтных комплектных устройств без учета их функций, полагая, что функции НКУ являются компетенцией проектировщиков электроустановки, частью которых эти НКУ являются.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
Классификация
>>>Действия
Синонимы
Сопутствующие термины
EN
- assembly
- electrical switchboard
- low voltage controlgear and assembly
- low voltage switchboard
- low voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
- low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
- LV switchgear and controlgear assembly
- LV switchgear assembly
- panel
- power switchgear and controlgear assembly
- PSC-assembly
- switchboard
- switchgear and controlgear
- switchgear/controlgear
DE
- Schaltanlagen und/oder Schaltgeräte
FR
распределительное устройство
Распределительным устройством (РУ) называется электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая сборные и соединительные шины, коммутационные аппараты, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[РД 34.20.185-94]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, предназначенная для приема и распределения электрической энергии на одном напряжении и содержащая коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные шины [секции шин], устройства управления и защиты.
Примечание. К устройствам управления относятся аппараты и связывающие их элементы обеспечивающие контроль, измерение, сигнализацию и выполнение команд.
[ ГОСТ 24291-90]
[ ГОСТ Р 53685-2009]
электрическое распределительное устройство
распределительное устройство
Устройство, предназначенное для приема и распределения электроэнергии на одном напряжении и содержащее коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные соединительные устройства.
Примечание. В состав распределительного устройства дополнительно могут входить устройства защиты и управления
[ОСТ 45.55-99]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая коммутационные аппараты, сборные и соединительные шины, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[ПОТ Р М-016-2001]
[РД 153-34.0-03.150-00]
устройство распределительное
Совокупность аппаратов и приборов для приёма и распределения электроэнергии одного напряжения, вырабатываемой электростанцией или преобразуемой подстанцией
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
switching substation
a substation which includes switchgear and usually busbars, but no power transformers
[IEV number 605-01-02]FR
poste de sectionnement
poste de coupure
poste comprenant des organes de manoeuvre et généralement des jeux de barres, à l'exclusion de transformateurs de puissance
[IEV number 605-01-02]В качестве РУ 6—10 кВ используется сборка высокого напряжения с однополюсными разъединителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения и одна камера КСО с выключателем нагрузки и предохранителями для подключения трансформатора. Для РУ 0,4 кВ применяются сборки низкого напряжения с предохранителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения.
На ПС применяются открытые (ОРУ), закрытые (ЗРУ) или комплектные (КРУ) распределительные устройства.
[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
В общем случае ПС и РУ являются составной частью электроустановок, которые различаются:
-
по назначению:
- генерирующие,
- преобразовательно-распределительные,
-
потребительские.
Генерирующие электроустановки служат для выработки электроэнергии, преобразовательно-распределительные электроустановки преобразуют электроэнергию в удобный для передачи и потребления вид, передают ее и распределяют между потребителями;
-
по роду тока:
- постоянного тока,
- переменного тока.
-
по напряжению:
- до 1000 В,
- выше 1000 В.
Шкала номинальных напряжений ограничена сравнительно небольшим числом стандартных значений, благодаря чему изготавливается небольшое число типоразмеров машин и оборудования, а электросети выполняются более экономичными. В установках трехфазного тока номинальным напряжением принято считать напряжение между фазами (междуфазовое напряжение). Согласно ГОСТ 29322—92 установлена следующая шкала номинальных напряжений:
для электросетей переменного тока частотой 50 Гц междуфазовое напряжение должно быть: 12, 24, 36, 42, 127, 220, 380 В; 3, 6, 10, 20, 35, 110, 150, 220, 330, 500, 750 и 1150 кВ;
для электросетей постоянного тока: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 110, 220, 440, 660, 825, 3000 В и выше.-
по способу присоединения к электросети ПС разделяются на:
- тупиковые (блочные),
- ответвительные (блочные),
- проходные (транзитные)
- узловые.
Тупиковые ПС получают питание по одной или двум тупиковым ВЛ.
Ответвительные ПС присоединяются ответвлением к одной или двум проходящим ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Проходные ПС включаются в рассечку одной или двух проходящих ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Узловые ПС кроме питающих имеют отходящие радиальные или транзитные ВЛ.-
по способу управления ПС могут быть:
- только с телесигнализацией,
- телеуправляемыми с телесигнализацией,
- с телесигнализацией и управлением с общеподстанционного пункта управления (ОПУ).
Подстанции оперативно обслуживаются постоянным дежурным персоналом на щите управления, дежурными на дому или оперативно-выездными бригадами (ОВБ). Ремонт ПС осуществляется специализированными выездными бригадами централизованного ремонта или местным персоналом подстанции.
В РУ напряжением до 1000 В провода, шины, аппараты, приборы и конструкции выбирают как по нормальным условиям работы (напряжению и току), так и по термическим и динамическим воздействиям токов коротких замыканий (КЗ) или предельно допустимой отключаемой мощности.
В РУ и ПС напряжением выше 1000 В расстояния между электрооборудованием, аппаратами, токоведущими частями, изоляторами, ограждениями и конструкциями устанавливаются так, чтобы при нормальном режиме работы электроустановки возникающие физические явления (температура нагрева, электрическая дуга, выброс газов, искрение и др.) не могли привести к повреждению оборудования и КЗ.[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
Several different classifications of switchgear can be made:- By the current rating.
-
By interrupting rating (maximum short circuit current that the device can safely interrupt)
- Circuit breakers can open and close on fault currents
- Load-break/Load-make switches can switch normal system load currents
- Isolators may only be operated while the circuit is dead, or the load current is very small.
-
By voltage class:
- Low voltage (less than 1,000 volts AC)
- Medium voltage (1,000–35,000 volts AC)
- High voltage (more than 35,000 volts AC)
-
By insulating medium:
-
By construction type:
- Indoor (further classified by IP (Ingress Protection) class or NEMA enclosure type)
- Outdoor
- Industrial
- Utility
- Marine
- Draw-out elements (removable without many tools)
- Fixed elements (bolted fasteners)
- Live-front
- Dead-front
- Open
- Metal-enclosed
- Metal-clad
- Metal enclosed & Metal clad
- Arc-resistant
-
By IEC degree of internal separation
- No Separation (Form 1)
- Busbars separated from functional units (Form 2a, 2b, 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from busbars (Form 2b, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from functional units but not from each other (Form 3a, 3b)
- Functional units separated from each other (Form 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from each other (Form 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separate from their associated functional unit (Form 4b)
-
By interrupting device:
-
By operating method:
- Manually operated
- Motor/stored energy operated
- Solenoid operated
-
By type of current:
-
By application:
-
By purpose
- Isolating switches (disconnectors)
- Load-break switches.
- Grounding (earthing) switches
A single line-up may incorporate several different types of devices, for example, air-insulated bus, vacuum circuit breakers, and manually operated switches may all exist in the same row of cubicles.
Ratings, design, specifications and details of switchgear are set by a multitude of standards. In North America mostly IEEE and ANSI standards are used, much of the rest of the world uses IEC standards, sometimes with local national derivatives or variations.
[Robert W. Smeaton (ed) Switchgear and Control Handbook 3rd Ed., Mc Graw Hill, new York 1997]
[ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High_voltage_switchgear]Тематики
- электрификация, электроснабж. железных дорог
- электроагрегаты генераторные
- электробезопасность
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
EN
- distribution
- energy distribution board
- gear
- switch-gear
- switchboard
- switchgear
- switching substation
- switchyard
DE
FR
распределительный щит
Комплектное устройство, содержащее различную коммутационную аппаратуру, соединенное с одной или более отходящими электрическими цепями, питающееся от одной или более входящих цепей, вместе с зажимами для присоединения нейтральных и защитных проводников.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
щит распределительный
Электротехническое устройство, объединяющее коммутационную, регулирующую и защитную аппаратуру, а также контрольно-измерительные и сигнальные приборы
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
распределительный щит
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]EN
distribution board
assembly containing different types of switchgear and controlgear associated with one or more outgoing electric circuits fed from one or more incoming electric circuits, together with terminals for the neutral and protective conductors.
[IEV number 826-16-08]FR
tableau de répartition, m
ensemble comportant différents types d'appareillage associés à un ou plusieurs circuits électriques de départ alimentés par un ou plusieurs circuits électriques d'arrivée, ainsi que des bornes pour les conducteurs neutre et de protection.
[IEV number 826-16-08]Distribution switchboards, including the Main LV Switchboard (MLVS), are critical to the dependability of an electrical installation. They must comply with well-defined standards governing the design and construction of LV switchgear assemblies
A distribution switchboard is the point at which an incoming-power supply divides into separate circuits, each of which is controlled and protected by the fuses or switchgear of the switchboard. A distribution switchboard is divided into a number of functional units, each comprising all the electrical and mechanical elements that contribute to the fulfilment of a given function. It represents a key link in the dependability chain.
Consequently, the type of distribution switchboard must be perfectly adapted to its application. Its design and construction must comply with applicable standards and working practises.
[Schneider Electric]Распределительные щиты, включая главный распределительный щит низкого напряжения (ГРЩ), играют решающую роль в обеспечении надежности электроустановки. Они должны отвечать требованиям соответствующих стандартов, определяющих конструкцию и порядок изготовления НКУ распределения электроэнергии.
В распределительном щите выполняется прием электроэнергии и ее распределение по отдельным цепям, каждая из которых контролируется и защищается плавкими предохранителями или автоматическими выключателями.
Распределительный щит состоит из функциональных блоков, включающих в себя все электрические и механические элементы, необходимые для выполнения требуемой функции. Распределительный щит представляет собой ключевое звено в цепи обеспечения надежности.
Тип распределительного щита должен соответствовать области применения. Конструкция и изготовление распределительного щита должны удовлетворять требованиям применимых стандартов и учитывать накопленную практику применения.
[Перевод Интент]
Рис. Schneider Electric
With Prisma Plus G you can be sure to build 100% Schneider Electric switchboards that are safe, optimised:
> All components (switchgear, distribution blocks, prefabricated connections, etc.) are perfectly rated and coordinated to work together;
> All switchboard configurations, even the most demanding ones, have been tested.
You can prove that your switchboard meets the current standards, at any time.
You can be sure to build a reliable electrical installation and give your customers full satisfaction in terms of dependability and safety for people and the installation.
Prisma Plus G with its discreet design, blends harmoniously into all tertiary and industrial buildings, including in entrance halls and passageways.
With Prisma Plus G you can build just the right switchboard for your customer, sized precisely to fit costs and needs.
With this complete, prefabricated and tested system, it's easy to upgrade your installation and still maintain the performance levels.
> The wall-mounted and floor-standing enclosures combine easily with switchboards already in service.
> Devices can be replaced or added at any time.
[Schneider Electric]С помощью оболочек Prisma Plus G можно создавать безопасные распределительные щиты, на 100 % состоящие из изделий Schneider Electric:
> все изделия (коммутационная аппаратура, распределительные блоки, готовые заводские соединения и т. д.) полностью совместимы механически и электрически;
> все варианты компоновки распределительных щитов, в том числе для наиболее ответственных применений, прошли испытания.В любое время вы можете доказать, что ваши распределительные щиты полностью соответствуют требованиям действующих стандартов.
Вы можете быть полностью уверены в том, что создаете надежные электроустановки, удовлетворяющие всем требованиям безопасности для людей и оборудования
Благодаря строгому дизайну, распределительные щиты Prisma Plus G гармонично сочетаются с интерьером любого общественного или промышленного здания. Они хорошо смотрятся и в вестибюле, и в коридоре.
Применяя оболочки Prisma Plus G можно создавать распределительные щиты, точно соответствующие требованиям заказчика как с точки зрения технических характеристик, так и стоимости.
С помощью данной испытанной системы, содержащей все необходимые компоненты заводского изготовления можно легко модернизировать существующую электроустановку и поддерживать её уровни производительности.> Навесные и напольные оболочки можно легко присоединить к уже эксплуатируемым распределительным щитам.
> Аппаратуру можно заменять или добавлять в любое время.
[Перевод Интент]The switchboard, central to the electrical installation.
Both the point of arrival of energy and a device for distribution to the site applications, the LV switchboard is the intelligence of the system, central to the electrical installation.
[Schneider Electric]Распределительный щит – «сердце» электроустановки.
Низковольтное комплектное устройство распределения является «сердцем» электроустановки, поскольку именно оно принимает электроэнергию из сети и распределяет её по территориально распределенным нагрузкам.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- электроснабжение в целом
EN
- branch distribution panel
- distributing board
- distributing panel
- distributing switchboard
- distribution bench
- distribution board
- distribution panel
- distribution switchboard
- gear
- keyboard
- PNL
- SB
- sw & d
- switchboard
- switchboard panel
DE
- elektrischer Verteiler, m
- Schalttafel
- Verteiler, m
FR
- tableau de distribution
- tableau de répartition, m
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > switchboard
-
8 gear
- распределительный щит
- распределительное устройство
- оборудование
- инструменты
- входить в сцепление
- аппаратура
аппаратура
-
[Интент]FR
-
виды аппаратуры
- низковольтная аппаратура
- аппаратура распределения
- аппаратура управления
- аппаратура распределения и управления
- аппаратура для цепей управления
- коммутационная аппаратура
- контрльно-измерительная аппаратура (КИП)
- электронная аппаратура
- радиоэлектронная аппаратура
- закрытая аппаратура без вентиляции, охлаждаемая естественной конвекцией воздуха
- закрытая вентилируемая аппаратура
- открытая аппаратура
- периферийная аппаратура
- переносная аппаратура
- портативная аппаратура
Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
EN
входить в сцепление
приводить в движение механизм
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
инструменты
орудия
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
оборудование
оборудование
Совокупность связанных между собой частей или устройств, из которых по крайней мере одно движется, а также элементы привода, управления и энергетические узлы, которые предназначены для определенного применения, в частности для обработки, производства, перемещения или упаковки материала. К термину «оборудование» относят также машину и совокупность машин, которые так устроены и управляемы, что они функционируют как единое целое для достижения одной и той же цели.
[ГОСТ ЕН 1070-2003]
-
[IEV number 151-11-25 ]
оборудование
Оснащение, материалы, приспособления, устройства, механизмы, приборы, инструменты и другие принадлежности, используемые в качестве частей электрической установки или в соединении с ней.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]EN
equipment
single apparatus or set of devices or apparatuses, or the set of main devices of an installation, or all devices necessary to perform a specific task
NOTE – Examples of equipment are a power transformer, the equipment of a substation, measuring equipment.
[IEV number 151-11-25 ]
equipment
material, fittings, devices, components, appliances, fixtures, apparatus, and the like used as part of, or in connection with, the electrical equipment of machines
[IEC 60204-1-2006]FR
équipement, m
matériel, m
appareil unique ou ensemble de dispositifs ou appareils, ou ensemble des dispositifs principaux d'une installation, ou ensemble des dispositifs nécessaires à l'accomplissement d'une tâche particulière
NOTE – Des exemples d’équipement ou de matériel sont un transformateur de puissance, l’équipement d’une sous-station, un équipement de mesure.
[IEV number 151-11-25]Тематики
EN
- accessories
- apparatus
- appliance
- assets
- environment
- equipment
- facility
- fitment
- fixing
- gear
- H/W
- hardware
- hardware environment
- HW
- installation
- instrument
- instrumentation
- layout
- machinery
- outfit
- paraphernalia
- plant
- plant stock
- product
- provisions
- rig
- rigging
- set-up
- stock-in-trade
- tackle
- technical equipment
- technique
DE
FR
- machine
- matériel, m
- équipement, m
распределительное устройство
Распределительным устройством (РУ) называется электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая сборные и соединительные шины, коммутационные аппараты, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[РД 34.20.185-94]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, предназначенная для приема и распределения электрической энергии на одном напряжении и содержащая коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные шины [секции шин], устройства управления и защиты.
Примечание. К устройствам управления относятся аппараты и связывающие их элементы обеспечивающие контроль, измерение, сигнализацию и выполнение команд.
[ ГОСТ 24291-90]
[ ГОСТ Р 53685-2009]
электрическое распределительное устройство
распределительное устройство
Устройство, предназначенное для приема и распределения электроэнергии на одном напряжении и содержащее коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные соединительные устройства.
Примечание. В состав распределительного устройства дополнительно могут входить устройства защиты и управления
[ОСТ 45.55-99]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая коммутационные аппараты, сборные и соединительные шины, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[ПОТ Р М-016-2001]
[РД 153-34.0-03.150-00]
устройство распределительное
Совокупность аппаратов и приборов для приёма и распределения электроэнергии одного напряжения, вырабатываемой электростанцией или преобразуемой подстанцией
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
switching substation
a substation which includes switchgear and usually busbars, but no power transformers
[IEV number 605-01-02]FR
poste de sectionnement
poste de coupure
poste comprenant des organes de manoeuvre et généralement des jeux de barres, à l'exclusion de transformateurs de puissance
[IEV number 605-01-02]В качестве РУ 6—10 кВ используется сборка высокого напряжения с однополюсными разъединителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения и одна камера КСО с выключателем нагрузки и предохранителями для подключения трансформатора. Для РУ 0,4 кВ применяются сборки низкого напряжения с предохранителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения.
На ПС применяются открытые (ОРУ), закрытые (ЗРУ) или комплектные (КРУ) распределительные устройства.
[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
В общем случае ПС и РУ являются составной частью электроустановок, которые различаются:
-
по назначению:
- генерирующие,
- преобразовательно-распределительные,
-
потребительские.
Генерирующие электроустановки служат для выработки электроэнергии, преобразовательно-распределительные электроустановки преобразуют электроэнергию в удобный для передачи и потребления вид, передают ее и распределяют между потребителями;
-
по роду тока:
- постоянного тока,
- переменного тока.
-
по напряжению:
- до 1000 В,
- выше 1000 В.
Шкала номинальных напряжений ограничена сравнительно небольшим числом стандартных значений, благодаря чему изготавливается небольшое число типоразмеров машин и оборудования, а электросети выполняются более экономичными. В установках трехфазного тока номинальным напряжением принято считать напряжение между фазами (междуфазовое напряжение). Согласно ГОСТ 29322—92 установлена следующая шкала номинальных напряжений:
для электросетей переменного тока частотой 50 Гц междуфазовое напряжение должно быть: 12, 24, 36, 42, 127, 220, 380 В; 3, 6, 10, 20, 35, 110, 150, 220, 330, 500, 750 и 1150 кВ;
для электросетей постоянного тока: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 110, 220, 440, 660, 825, 3000 В и выше.-
по способу присоединения к электросети ПС разделяются на:
- тупиковые (блочные),
- ответвительные (блочные),
- проходные (транзитные)
- узловые.
Тупиковые ПС получают питание по одной или двум тупиковым ВЛ.
Ответвительные ПС присоединяются ответвлением к одной или двум проходящим ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Проходные ПС включаются в рассечку одной или двух проходящих ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Узловые ПС кроме питающих имеют отходящие радиальные или транзитные ВЛ.-
по способу управления ПС могут быть:
- только с телесигнализацией,
- телеуправляемыми с телесигнализацией,
- с телесигнализацией и управлением с общеподстанционного пункта управления (ОПУ).
Подстанции оперативно обслуживаются постоянным дежурным персоналом на щите управления, дежурными на дому или оперативно-выездными бригадами (ОВБ). Ремонт ПС осуществляется специализированными выездными бригадами централизованного ремонта или местным персоналом подстанции.
В РУ напряжением до 1000 В провода, шины, аппараты, приборы и конструкции выбирают как по нормальным условиям работы (напряжению и току), так и по термическим и динамическим воздействиям токов коротких замыканий (КЗ) или предельно допустимой отключаемой мощности.
В РУ и ПС напряжением выше 1000 В расстояния между электрооборудованием, аппаратами, токоведущими частями, изоляторами, ограждениями и конструкциями устанавливаются так, чтобы при нормальном режиме работы электроустановки возникающие физические явления (температура нагрева, электрическая дуга, выброс газов, искрение и др.) не могли привести к повреждению оборудования и КЗ.[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
Several different classifications of switchgear can be made:- By the current rating.
-
By interrupting rating (maximum short circuit current that the device can safely interrupt)
- Circuit breakers can open and close on fault currents
- Load-break/Load-make switches can switch normal system load currents
- Isolators may only be operated while the circuit is dead, or the load current is very small.
-
By voltage class:
- Low voltage (less than 1,000 volts AC)
- Medium voltage (1,000–35,000 volts AC)
- High voltage (more than 35,000 volts AC)
-
By insulating medium:
-
By construction type:
- Indoor (further classified by IP (Ingress Protection) class or NEMA enclosure type)
- Outdoor
- Industrial
- Utility
- Marine
- Draw-out elements (removable without many tools)
- Fixed elements (bolted fasteners)
- Live-front
- Dead-front
- Open
- Metal-enclosed
- Metal-clad
- Metal enclosed & Metal clad
- Arc-resistant
-
By IEC degree of internal separation
- No Separation (Form 1)
- Busbars separated from functional units (Form 2a, 2b, 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from busbars (Form 2b, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from functional units but not from each other (Form 3a, 3b)
- Functional units separated from each other (Form 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from each other (Form 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separate from their associated functional unit (Form 4b)
-
By interrupting device:
-
By operating method:
- Manually operated
- Motor/stored energy operated
- Solenoid operated
-
By type of current:
-
By application:
-
By purpose
- Isolating switches (disconnectors)
- Load-break switches.
- Grounding (earthing) switches
A single line-up may incorporate several different types of devices, for example, air-insulated bus, vacuum circuit breakers, and manually operated switches may all exist in the same row of cubicles.
Ratings, design, specifications and details of switchgear are set by a multitude of standards. In North America mostly IEEE and ANSI standards are used, much of the rest of the world uses IEC standards, sometimes with local national derivatives or variations.
[Robert W. Smeaton (ed) Switchgear and Control Handbook 3rd Ed., Mc Graw Hill, new York 1997]
[ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High_voltage_switchgear]Тематики
- электрификация, электроснабж. железных дорог
- электроагрегаты генераторные
- электробезопасность
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
EN
- distribution
- energy distribution board
- gear
- switch-gear
- switchboard
- switchgear
- switching substation
- switchyard
DE
FR
распределительный щит
Комплектное устройство, содержащее различную коммутационную аппаратуру, соединенное с одной или более отходящими электрическими цепями, питающееся от одной или более входящих цепей, вместе с зажимами для присоединения нейтральных и защитных проводников.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
щит распределительный
Электротехническое устройство, объединяющее коммутационную, регулирующую и защитную аппаратуру, а также контрольно-измерительные и сигнальные приборы
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
распределительный щит
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]EN
distribution board
assembly containing different types of switchgear and controlgear associated with one or more outgoing electric circuits fed from one or more incoming electric circuits, together with terminals for the neutral and protective conductors.
[IEV number 826-16-08]FR
tableau de répartition, m
ensemble comportant différents types d'appareillage associés à un ou plusieurs circuits électriques de départ alimentés par un ou plusieurs circuits électriques d'arrivée, ainsi que des bornes pour les conducteurs neutre et de protection.
[IEV number 826-16-08]Distribution switchboards, including the Main LV Switchboard (MLVS), are critical to the dependability of an electrical installation. They must comply with well-defined standards governing the design and construction of LV switchgear assemblies
A distribution switchboard is the point at which an incoming-power supply divides into separate circuits, each of which is controlled and protected by the fuses or switchgear of the switchboard. A distribution switchboard is divided into a number of functional units, each comprising all the electrical and mechanical elements that contribute to the fulfilment of a given function. It represents a key link in the dependability chain.
Consequently, the type of distribution switchboard must be perfectly adapted to its application. Its design and construction must comply with applicable standards and working practises.
[Schneider Electric]Распределительные щиты, включая главный распределительный щит низкого напряжения (ГРЩ), играют решающую роль в обеспечении надежности электроустановки. Они должны отвечать требованиям соответствующих стандартов, определяющих конструкцию и порядок изготовления НКУ распределения электроэнергии.
В распределительном щите выполняется прием электроэнергии и ее распределение по отдельным цепям, каждая из которых контролируется и защищается плавкими предохранителями или автоматическими выключателями.
Распределительный щит состоит из функциональных блоков, включающих в себя все электрические и механические элементы, необходимые для выполнения требуемой функции. Распределительный щит представляет собой ключевое звено в цепи обеспечения надежности.
Тип распределительного щита должен соответствовать области применения. Конструкция и изготовление распределительного щита должны удовлетворять требованиям применимых стандартов и учитывать накопленную практику применения.
[Перевод Интент]
Рис. Schneider Electric
With Prisma Plus G you can be sure to build 100% Schneider Electric switchboards that are safe, optimised:
> All components (switchgear, distribution blocks, prefabricated connections, etc.) are perfectly rated and coordinated to work together;
> All switchboard configurations, even the most demanding ones, have been tested.
You can prove that your switchboard meets the current standards, at any time.
You can be sure to build a reliable electrical installation and give your customers full satisfaction in terms of dependability and safety for people and the installation.
Prisma Plus G with its discreet design, blends harmoniously into all tertiary and industrial buildings, including in entrance halls and passageways.
With Prisma Plus G you can build just the right switchboard for your customer, sized precisely to fit costs and needs.
With this complete, prefabricated and tested system, it's easy to upgrade your installation and still maintain the performance levels.
> The wall-mounted and floor-standing enclosures combine easily with switchboards already in service.
> Devices can be replaced or added at any time.
[Schneider Electric]С помощью оболочек Prisma Plus G можно создавать безопасные распределительные щиты, на 100 % состоящие из изделий Schneider Electric:
> все изделия (коммутационная аппаратура, распределительные блоки, готовые заводские соединения и т. д.) полностью совместимы механически и электрически;
> все варианты компоновки распределительных щитов, в том числе для наиболее ответственных применений, прошли испытания.В любое время вы можете доказать, что ваши распределительные щиты полностью соответствуют требованиям действующих стандартов.
Вы можете быть полностью уверены в том, что создаете надежные электроустановки, удовлетворяющие всем требованиям безопасности для людей и оборудования
Благодаря строгому дизайну, распределительные щиты Prisma Plus G гармонично сочетаются с интерьером любого общественного или промышленного здания. Они хорошо смотрятся и в вестибюле, и в коридоре.
Применяя оболочки Prisma Plus G можно создавать распределительные щиты, точно соответствующие требованиям заказчика как с точки зрения технических характеристик, так и стоимости.
С помощью данной испытанной системы, содержащей все необходимые компоненты заводского изготовления можно легко модернизировать существующую электроустановку и поддерживать её уровни производительности.> Навесные и напольные оболочки можно легко присоединить к уже эксплуатируемым распределительным щитам.
> Аппаратуру можно заменять или добавлять в любое время.
[Перевод Интент]The switchboard, central to the electrical installation.
Both the point of arrival of energy and a device for distribution to the site applications, the LV switchboard is the intelligence of the system, central to the electrical installation.
[Schneider Electric]Распределительный щит – «сердце» электроустановки.
Низковольтное комплектное устройство распределения является «сердцем» электроустановки, поскольку именно оно принимает электроэнергию из сети и распределяет её по территориально распределенным нагрузкам.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- электроснабжение в целом
EN
- branch distribution panel
- distributing board
- distributing panel
- distributing switchboard
- distribution bench
- distribution board
- distribution panel
- distribution switchboard
- gear
- keyboard
- PNL
- SB
- sw & d
- switchboard
- switchboard panel
DE
- elektrischer Verteiler, m
- Schalttafel
- Verteiler, m
FR
- tableau de distribution
- tableau de répartition, m
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > gear
-
9 conduit
изоляционная трубка
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
кабелепровод
Любой канал, обеспечивающий прокладку кабелей, в том числе, металлические и пластмассовые трубопроводы, рукава, каналы в полах, сотовые фальшполы, сетчатые лотки, желоба и кабель каналы (ISO/IEC 11801).
[ http://www.iks-media.ru/glossary/index.html?glossid=2400324]
кабелепровод
трасса
кабельный канал
Трасса или структура, предназначенная или используемая для прокладки и монтажа телекоммуникационных кабелей.
[ http://www.lanmaster.ru/SKS/DOKUMENT/568b.htm]Тематики
- СКС (структурированные кабельные системы)
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
EN
кабельная канализация
—
[Л.Г.Суменко. Англо-русский словарь по информационным технологиям. М.: ГП ЦНИИС, 2003.]Тематики
EN
кабельный канал
Кабельным каналом называется закрытое и заглубленное (частично или полностью) в грунт, пол, перекрытие и т. п. непроходное сооружение, предназначенное для размещения в нем кабелей, укладку, осмотр и ремонт которых возможно производить лишь при снятом перекрытии.
[ПУЭ. Раздел 2]
кабельный канал
Элемент системы электропроводки, расположенный над землей или полом или в земле или в полу, открытый, вентилируемый или замкнутый, размеры которого не позволяют вход людей, но обеспечивают доступ к трубам и (или) кабелям по всей длине в процессе монтажа и после него.
Примечание - Кабельный канал может составлять или не составлять часть конструкции здания
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
канал кабельный
Подземный непроходной канал, предназначенный для размещения электрических кабелей
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
cable channel
element of a wiring system above or in the ground or floor, open, ventilated or closed, and having dimensions which do not permit the entry of persons but allow access to the conduits and/or cables throughout their length during and after installation
NOTE – A cable channel may or may not form part of the building construction.
[IEV number 826-15-06]FR
caniveau, m
élément de canalisation situé au-dessus ou dans le sol ou le plancher, ouvert, ventilé ou fermé, ayant des dimensions ne permettant pas aux personnes d'y circuler, mais dans lequel les conduits ou câbles sont accessibles sur toute leur longueur, pendant et après installation
NOTE – Un caniveau peut ou non faire partie de la construction du bâtiment.
[IEV number 826-15-06]
Кабельные каналы:
а — лотковый типа ЛК; б — из сборных плит типа СК:1 — лоток; 2 — плита перекрытия; 3 — подготовка; 4 — плита стеновая; 5 — основание
Высота кабельных каналов в свету не ограничивается, но бывает не более 1200 мм. Ширина каналов определяется в зависимости от размеров применяемых кабельных конструкций из условия сохранения прохода не менее 300 мм при глубине канала до 600 мм, 450 мм — от более 600 до 900 мм, 600 мм при более 900 мм.
Полы в каналах выполняют с уклоном не менее 0,5% в сторону водосборников или ливневой канализации.
Для крепления кабельных конструкций в стенах каналов через каждые 0,8—1 м (по длине) устанавливают закладные детали. При заводском изготовлении стеновых панелей детали устанавливают на предприятии-изготовителе. Закладные детали в каналах глубиной до 600 мм располагают в один ряд, при большей глубине каналов — в два ряда.
В местах поворота и разветвления трассы устраивают уширительные камеры, размеры которых выбирают с учетом допускаемого радиуса изгиба прокладываемого кабеля.
[ http://forca.ru/knigi/oborudovanie/priemka-zdaniy-i-sooruzheniy-pod-montazh-elektrooborudovaniya-11.html]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Примечание(1)- Мнение автора карточкиТематики
- кабели, провода...
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
- электроустановки
Обобщающие термины
EN
- cable channel
- cable duct
- cable trench
- cabling
- conduit
- duct
- electric raceway
- raceway
- trench for cabling
DE
FR
- caniveau du câble
- caniveau, m
- conduite du câble
труба
Компонентзащищеннойтрубной электропроводки, имеющий, как правило, круглое поперечное сечение, предназначенный для прокладки изолированных проводов и(или) кабелей в электрических или коммуникационных установках, допускающий их затяжку в него и(или) их замену.
ПримечаниеСоединения труб должны быть достаточно плотными, чтобы изолированные провода и (или) кабели могли быть только затянуты, но не введены сбоку в просвет между трубами.
Трубы должны располагаться достаточно близко друг от друга, так чтобы отсутствовала возможность затянуть изолированные провода и (или) кабели в просвет между ними.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
трубопроводтруба
Закрытый элемент кабельной конструкцииКомпонент трубной электропроводки круглого или иного сечения для прокладки в электрических установках кабелей и/или изолированных проводови/или кабелей в электрических установках,позволяющий производить ихвыемкузатяжку и/или замену.
Примечание
Трубопроводы должны быть закрыты таким образом, чтобы имелась возможность вставлять в них изолированные провода и/или кабели.
Трубы должны располагаться достаточно близко друг от друга, так чтобы отсутствовала возможность затянуть изолированные провода и (или) кабели в просвет между ними.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]
Примечание. Синим цветом обозначен вариант, предлагаемый автором карточки.EN
conduit
a part of a closed wiring system of generally circular cross section for insulated conductors and/or cables in electrical or communication installations, allowing them to be drawn in and/or replaced
Source: 826-06-03 MOD
[IEV number 442-02-03]
conduit
part of a closed wiring system of circular or non-circular cross-section for insulated conductors and/or cables in electrical installations, allowing them to be drawn in and/or replaced
NOTE Conduits should be sufficiently close-jointed so that the insulated conductors and/or cables can only be drawn in and not inserted laterally.
[IEV 826-06-03]
[IEC 60204-1-2006]
raceway
A tube that encloses and protects electric wires.
[ http://www.answers.com/topic/raceway]FR
conduit
élément d'un système de canalisation fermé de section droite généralement circulaire, destiné à la mise en place par tirage ou au remplacement des conducteurs ou des câbles isolés dans les installations électriques ou de télécommunication
Source: 826-06-03 MOD
[IEV number 442-02-03]См. также пластмассовые трубы для электропроводок
См. также стальные трубы для электропроводок
4.1. Для прокладки проводов и кабелей необходимо применять специальные трубы для электропроводок: гладкие из непластифицированного ПВХ по ТУ 6-19-215-86, прил. 2; гладкие из вторичного ПЭ по ТУ 63.178-103-85, прил. 3; гладкие из наполненного ПЭ по ТУ 6-19-051-575-85, прил. 4; гофрированные из НПВХ по ТУ 6-19-051-419-84, прил. 5; гофрированные из ПЭ по ТУ 6-19-051-518-87, прил.6; гофрированные из вторичного ПЭ по ТУ 63.178-117-87, прил.7. При отсутствии указанных труб применяют технологические трубы: гладкие напорные из НПВХ по ТУ 6-19-231-87, прил.8; гладкие напорные из ПЭ низкого и высокого давления по ГОСТ 18599-83, прил. 9; гладкие из ПП по ТУ 38-102-100-76, прил. 10; трубы из вторичного ПЭ по ТУ 6-19-133-79, прил. П.
...
4.3. Применяют также трубы стальные электросварные по ГОСТ 10704-76 сортамент, прил. 12, легкие и обыкновенные водогазопроводные по ГОСТ 3262-75*, прил.13.[Министерство архитектуры, строительства и жилищно-коммунального хозяйства. Концерн «ЭЛЕКТРОМОНТАЖ». Инструкция по монтажу электропроводок в трубах]
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Примечание(1)- Мнение автора карточкиТематики
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > conduit
-
10 switchgear
- распределительное устройство
- коммутационное устройство
- коммутационная аппаратура
- аппаратура распределения
аппаратура распределения
Общий термин для коммутационных аппаратов и их комбинаций с относящимися к ним устройствами управления, измерения, защиты и регулирования, а также для узлов, в которых такие аппараты и устройства соединяются с соответствующими фидерами, комплектующим оборудованием, оболочками и опорными конструкциями, предназначенных, в принципе, для использования в системах производства, передачи, распределения и преобразования электрической энергии.
МЭК 60050(441-11-02).
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]EN
switchgear
a general term covering switching devices and their combination with associated control, measuring, protective and regulating equipment, also assemblies of such devices and equipment with associated interconnections, accessories, enclosures and supporting structures, intended in principle for use in connection with generation, transmission, distribution and conversion of electric energy
[IEV number 441-11-02]FR
appareillage de connexion
terme général applicable aux appareils de connexion et à leur combinaison avec des appareils de commande, de mesure, de protection et de réglage qui leur sont associés, ainsi qu'aux ensembles de tels appareils avec les connexions, les accessoires, les enveloppes et les supports correspondants, destinés en principe à être utilisés dans le domaine de la production, du transport, de la distribution et de la transformation de l'énergie électrique
[IEV number 441-11-02]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
EN
DE
- Schaltanlagen und/oder Schaltgeräte für Energieverteilung
FR
коммутационная аппаратура
коммутационное оборудование
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
коммутационное устройство
Устройство, предназначенное для обеспечения или прерывания подачи электрического тока в электрические цепи.
Примечание - Коммутационное устройство может выполнять одну или обе эти функции.
[ГОСТ ЕН 1070-2003]
коммутационное устройство
-
[IEV number 442-01-46]EN
switching device
a device designed to make or break the current in one or more electric circuits
Source: 441-14-01 MOD
[IEV number 442-01-46]
switchgear
any of several devices used for opening and closing electric circuits, esp those that pass high currents
[Collins]FR
dispositif de coupure
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
appareil destiné à établir ou à interrompre le courant dans un ou plusieurs circuits électriques
Source: 441-14-01 MOD
[IEV number 442-01-46]distribution board
assembly containing different types of switchgear and controlgear associated with one or more outgoing electric circuits fed from one or more incoming electric circuits, together with terminals for the neutral and protective conductors.
[IEV number 826-16-08]распределительная панель
НКУ, состоящее из коммутационных устройств или устройств защиты (например, плавких предохранителей), присоединенных к одной или нескольким выходным цепям с питанием от одной или нескольких входящих цепей, а также зажимов для нейтрального проводника и проводников цепей защиты. Оно может также содержать сигнальные устройства и другие устройства контроля.
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 3-99 ( МЭК 60439-3-90)]
Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
EN
DE
FR
распределительное устройство
Распределительным устройством (РУ) называется электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая сборные и соединительные шины, коммутационные аппараты, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[РД 34.20.185-94]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, предназначенная для приема и распределения электрической энергии на одном напряжении и содержащая коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные шины [секции шин], устройства управления и защиты.
Примечание. К устройствам управления относятся аппараты и связывающие их элементы обеспечивающие контроль, измерение, сигнализацию и выполнение команд.
[ ГОСТ 24291-90]
[ ГОСТ Р 53685-2009]
электрическое распределительное устройство
распределительное устройство
Устройство, предназначенное для приема и распределения электроэнергии на одном напряжении и содержащее коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные соединительные устройства.
Примечание. В состав распределительного устройства дополнительно могут входить устройства защиты и управления
[ОСТ 45.55-99]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая коммутационные аппараты, сборные и соединительные шины, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[ПОТ Р М-016-2001]
[РД 153-34.0-03.150-00]
устройство распределительное
Совокупность аппаратов и приборов для приёма и распределения электроэнергии одного напряжения, вырабатываемой электростанцией или преобразуемой подстанцией
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
switching substation
a substation which includes switchgear and usually busbars, but no power transformers
[IEV number 605-01-02]FR
poste de sectionnement
poste de coupure
poste comprenant des organes de manoeuvre et généralement des jeux de barres, à l'exclusion de transformateurs de puissance
[IEV number 605-01-02]В качестве РУ 6—10 кВ используется сборка высокого напряжения с однополюсными разъединителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения и одна камера КСО с выключателем нагрузки и предохранителями для подключения трансформатора. Для РУ 0,4 кВ применяются сборки низкого напряжения с предохранителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения.
На ПС применяются открытые (ОРУ), закрытые (ЗРУ) или комплектные (КРУ) распределительные устройства.
[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
В общем случае ПС и РУ являются составной частью электроустановок, которые различаются:
-
по назначению:
- генерирующие,
- преобразовательно-распределительные,
-
потребительские.
Генерирующие электроустановки служат для выработки электроэнергии, преобразовательно-распределительные электроустановки преобразуют электроэнергию в удобный для передачи и потребления вид, передают ее и распределяют между потребителями;
-
по роду тока:
- постоянного тока,
- переменного тока.
-
по напряжению:
- до 1000 В,
- выше 1000 В.
Шкала номинальных напряжений ограничена сравнительно небольшим числом стандартных значений, благодаря чему изготавливается небольшое число типоразмеров машин и оборудования, а электросети выполняются более экономичными. В установках трехфазного тока номинальным напряжением принято считать напряжение между фазами (междуфазовое напряжение). Согласно ГОСТ 29322—92 установлена следующая шкала номинальных напряжений:
для электросетей переменного тока частотой 50 Гц междуфазовое напряжение должно быть: 12, 24, 36, 42, 127, 220, 380 В; 3, 6, 10, 20, 35, 110, 150, 220, 330, 500, 750 и 1150 кВ;
для электросетей постоянного тока: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 110, 220, 440, 660, 825, 3000 В и выше.-
по способу присоединения к электросети ПС разделяются на:
- тупиковые (блочные),
- ответвительные (блочные),
- проходные (транзитные)
- узловые.
Тупиковые ПС получают питание по одной или двум тупиковым ВЛ.
Ответвительные ПС присоединяются ответвлением к одной или двум проходящим ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Проходные ПС включаются в рассечку одной или двух проходящих ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Узловые ПС кроме питающих имеют отходящие радиальные или транзитные ВЛ.-
по способу управления ПС могут быть:
- только с телесигнализацией,
- телеуправляемыми с телесигнализацией,
- с телесигнализацией и управлением с общеподстанционного пункта управления (ОПУ).
Подстанции оперативно обслуживаются постоянным дежурным персоналом на щите управления, дежурными на дому или оперативно-выездными бригадами (ОВБ). Ремонт ПС осуществляется специализированными выездными бригадами централизованного ремонта или местным персоналом подстанции.
В РУ напряжением до 1000 В провода, шины, аппараты, приборы и конструкции выбирают как по нормальным условиям работы (напряжению и току), так и по термическим и динамическим воздействиям токов коротких замыканий (КЗ) или предельно допустимой отключаемой мощности.
В РУ и ПС напряжением выше 1000 В расстояния между электрооборудованием, аппаратами, токоведущими частями, изоляторами, ограждениями и конструкциями устанавливаются так, чтобы при нормальном режиме работы электроустановки возникающие физические явления (температура нагрева, электрическая дуга, выброс газов, искрение и др.) не могли привести к повреждению оборудования и КЗ.[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
Several different classifications of switchgear can be made:- By the current rating.
-
By interrupting rating (maximum short circuit current that the device can safely interrupt)
- Circuit breakers can open and close on fault currents
- Load-break/Load-make switches can switch normal system load currents
- Isolators may only be operated while the circuit is dead, or the load current is very small.
-
By voltage class:
- Low voltage (less than 1,000 volts AC)
- Medium voltage (1,000–35,000 volts AC)
- High voltage (more than 35,000 volts AC)
-
By insulating medium:
-
By construction type:
- Indoor (further classified by IP (Ingress Protection) class or NEMA enclosure type)
- Outdoor
- Industrial
- Utility
- Marine
- Draw-out elements (removable without many tools)
- Fixed elements (bolted fasteners)
- Live-front
- Dead-front
- Open
- Metal-enclosed
- Metal-clad
- Metal enclosed & Metal clad
- Arc-resistant
-
By IEC degree of internal separation
- No Separation (Form 1)
- Busbars separated from functional units (Form 2a, 2b, 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from busbars (Form 2b, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from functional units but not from each other (Form 3a, 3b)
- Functional units separated from each other (Form 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from each other (Form 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separate from their associated functional unit (Form 4b)
-
By interrupting device:
-
By operating method:
- Manually operated
- Motor/stored energy operated
- Solenoid operated
-
By type of current:
-
By application:
-
By purpose
- Isolating switches (disconnectors)
- Load-break switches.
- Grounding (earthing) switches
A single line-up may incorporate several different types of devices, for example, air-insulated bus, vacuum circuit breakers, and manually operated switches may all exist in the same row of cubicles.
Ratings, design, specifications and details of switchgear are set by a multitude of standards. In North America mostly IEEE and ANSI standards are used, much of the rest of the world uses IEC standards, sometimes with local national derivatives or variations.
[Robert W. Smeaton (ed) Switchgear and Control Handbook 3rd Ed., Mc Graw Hill, new York 1997]
[ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High_voltage_switchgear]Тематики
- электрификация, электроснабж. железных дорог
- электроагрегаты генераторные
- электробезопасность
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
EN
- distribution
- energy distribution board
- gear
- switch-gear
- switchboard
- switchgear
- switching substation
- switchyard
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > switchgear
-
11 courant admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant admissible, m
-
12 courant permanent admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant permanent admissible, m
-
13 Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
-
14 Strombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Strombelastbarkeit, f
-
15 continuous current-carrying capacity
длительная пропускная способность по току
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > continuous current-carrying capacity
-
16 ampacity (US)
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > ampacity (US)
-
17 continuous current
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
непрерывный ток
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > continuous current
-
18 current-carrying capacity
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
предельно допустимый ток
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
прочность печатной платы к токовой нагрузке
Свойство печатной платы сохранять электрические и механические характеристики после воздействия максимально допустимой токовой нагрузки на печатный проводник или металлизированное отверстие печатной платы.
[ ГОСТ Р 53386-2009]Тематики
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > current-carrying capacity
-
19 conduit
труба
Компонентзащищеннойтрубной электропроводки, имеющий, как правило, круглое поперечное сечение, предназначенный для прокладки изолированных проводов и(или) кабелей в электрических или коммуникационных установках, допускающий их затяжку в него и(или) их замену.
ПримечаниеСоединения труб должны быть достаточно плотными, чтобы изолированные провода и (или) кабели могли быть только затянуты, но не введены сбоку в просвет между трубами.
Трубы должны располагаться достаточно близко друг от друга, так чтобы отсутствовала возможность затянуть изолированные провода и (или) кабели в просвет между ними.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
трубопроводтруба
Закрытый элемент кабельной конструкцииКомпонент трубной электропроводки круглого или иного сечения для прокладки в электрических установках кабелей и/или изолированных проводови/или кабелей в электрических установках,позволяющий производить ихвыемкузатяжку и/или замену.
Примечание
Трубопроводы должны быть закрыты таким образом, чтобы имелась возможность вставлять в них изолированные провода и/или кабели.
Трубы должны располагаться достаточно близко друг от друга, так чтобы отсутствовала возможность затянуть изолированные провода и (или) кабели в просвет между ними.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]
Примечание. Синим цветом обозначен вариант, предлагаемый автором карточки.EN
conduit
a part of a closed wiring system of generally circular cross section for insulated conductors and/or cables in electrical or communication installations, allowing them to be drawn in and/or replaced
Source: 826-06-03 MOD
[IEV number 442-02-03]
conduit
part of a closed wiring system of circular or non-circular cross-section for insulated conductors and/or cables in electrical installations, allowing them to be drawn in and/or replaced
NOTE Conduits should be sufficiently close-jointed so that the insulated conductors and/or cables can only be drawn in and not inserted laterally.
[IEV 826-06-03]
[IEC 60204-1-2006]
raceway
A tube that encloses and protects electric wires.
[ http://www.answers.com/topic/raceway]FR
conduit
élément d'un système de canalisation fermé de section droite généralement circulaire, destiné à la mise en place par tirage ou au remplacement des conducteurs ou des câbles isolés dans les installations électriques ou de télécommunication
Source: 826-06-03 MOD
[IEV number 442-02-03]См. также пластмассовые трубы для электропроводок
См. также стальные трубы для электропроводок
4.1. Для прокладки проводов и кабелей необходимо применять специальные трубы для электропроводок: гладкие из непластифицированного ПВХ по ТУ 6-19-215-86, прил. 2; гладкие из вторичного ПЭ по ТУ 63.178-103-85, прил. 3; гладкие из наполненного ПЭ по ТУ 6-19-051-575-85, прил. 4; гофрированные из НПВХ по ТУ 6-19-051-419-84, прил. 5; гофрированные из ПЭ по ТУ 6-19-051-518-87, прил.6; гофрированные из вторичного ПЭ по ТУ 63.178-117-87, прил.7. При отсутствии указанных труб применяют технологические трубы: гладкие напорные из НПВХ по ТУ 6-19-231-87, прил.8; гладкие напорные из ПЭ низкого и высокого давления по ГОСТ 18599-83, прил. 9; гладкие из ПП по ТУ 38-102-100-76, прил. 10; трубы из вторичного ПЭ по ТУ 6-19-133-79, прил. П.
...
4.3. Применяют также трубы стальные электросварные по ГОСТ 10704-76 сортамент, прил. 12, легкие и обыкновенные водогазопроводные по ГОСТ 3262-75*, прил.13.[Министерство архитектуры, строительства и жилищно-коммунального хозяйства. Концерн «ЭЛЕКТРОМОНТАЖ». Инструкция по монтажу электропроводок в трубах]
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Примечание(1)- Мнение автора карточкиТематики
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > conduit
-
20 Elektroinstallationsrohr
труба
Компонентзащищеннойтрубной электропроводки, имеющий, как правило, круглое поперечное сечение, предназначенный для прокладки изолированных проводов и(или) кабелей в электрических или коммуникационных установках, допускающий их затяжку в него и(или) их замену.
ПримечаниеСоединения труб должны быть достаточно плотными, чтобы изолированные провода и (или) кабели могли быть только затянуты, но не введены сбоку в просвет между трубами.
Трубы должны располагаться достаточно близко друг от друга, так чтобы отсутствовала возможность затянуть изолированные провода и (или) кабели в просвет между ними.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
трубопроводтруба
Закрытый элемент кабельной конструкцииКомпонент трубной электропроводки круглого или иного сечения для прокладки в электрических установках кабелей и/или изолированных проводови/или кабелей в электрических установках,позволяющий производить ихвыемкузатяжку и/или замену.
Примечание
Трубопроводы должны быть закрыты таким образом, чтобы имелась возможность вставлять в них изолированные провода и/или кабели.
Трубы должны располагаться достаточно близко друг от друга, так чтобы отсутствовала возможность затянуть изолированные провода и (или) кабели в просвет между ними.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]
Примечание. Синим цветом обозначен вариант, предлагаемый автором карточки.EN
conduit
a part of a closed wiring system of generally circular cross section for insulated conductors and/or cables in electrical or communication installations, allowing them to be drawn in and/or replaced
Source: 826-06-03 MOD
[IEV number 442-02-03]
conduit
part of a closed wiring system of circular or non-circular cross-section for insulated conductors and/or cables in electrical installations, allowing them to be drawn in and/or replaced
NOTE Conduits should be sufficiently close-jointed so that the insulated conductors and/or cables can only be drawn in and not inserted laterally.
[IEV 826-06-03]
[IEC 60204-1-2006]
raceway
A tube that encloses and protects electric wires.
[ http://www.answers.com/topic/raceway]FR
conduit
élément d'un système de canalisation fermé de section droite généralement circulaire, destiné à la mise en place par tirage ou au remplacement des conducteurs ou des câbles isolés dans les installations électriques ou de télécommunication
Source: 826-06-03 MOD
[IEV number 442-02-03]См. также пластмассовые трубы для электропроводок
См. также стальные трубы для электропроводок
4.1. Для прокладки проводов и кабелей необходимо применять специальные трубы для электропроводок: гладкие из непластифицированного ПВХ по ТУ 6-19-215-86, прил. 2; гладкие из вторичного ПЭ по ТУ 63.178-103-85, прил. 3; гладкие из наполненного ПЭ по ТУ 6-19-051-575-85, прил. 4; гофрированные из НПВХ по ТУ 6-19-051-419-84, прил. 5; гофрированные из ПЭ по ТУ 6-19-051-518-87, прил.6; гофрированные из вторичного ПЭ по ТУ 63.178-117-87, прил.7. При отсутствии указанных труб применяют технологические трубы: гладкие напорные из НПВХ по ТУ 6-19-231-87, прил.8; гладкие напорные из ПЭ низкого и высокого давления по ГОСТ 18599-83, прил. 9; гладкие из ПП по ТУ 38-102-100-76, прил. 10; трубы из вторичного ПЭ по ТУ 6-19-133-79, прил. П.
...
4.3. Применяют также трубы стальные электросварные по ГОСТ 10704-76 сортамент, прил. 12, легкие и обыкновенные водогазопроводные по ГОСТ 3262-75*, прил.13.[Министерство архитектуры, строительства и жилищно-коммунального хозяйства. Концерн «ЭЛЕКТРОМОНТАЖ». Инструкция по монтажу электропроводок в трубах]
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Примечание(1)- Мнение автора карточкиТематики
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Elektroinstallationsrohr
- 1
- 2
См. также в других словарях:
electric motor — motor (def. 4). [1885 90] * * * Introduction any of a class of devices that convert electrical energy to mechanical energy, usually by employing electromagnetic phenomena. Most electric motors develop their mechanical torque by the… … Universalium
electric generator — ▪ instrument Introduction also called dynamo, any machine that converts mechanical energy to electricity for transmission and distribution over power lines to domestic, commercial, and industrial customers. Generators also produce the… … Universalium
Electric power distribution — … Wikipedia
Electric motor — For other kinds of motors, see motor (disambiguation). For a railroad electric engine, see electric locomotive. Various electric motors. A 9 volt PP3 transistor battery is in the center foreground for size comparison. An electric motor converts… … Wikipedia
Electric shock — Electrocute redirects here. For the band, see Electrocute (band). An electric shock can occur upon contact of a human s body with any source of voltage high enough to cause sufficient current through the muscles or hair. The minimum current a… … Wikipedia
Electric vehicle — Sustainable energy Renewable energy … Wikipedia
Mineral-insulated copper-clad cable — MIMS redirects here. For multi isotope imaging mass spectrometry, see Isotope mass spectrometry. PVC sheathed MICC cable. Conductor cross section area is 1.5 mm²; overall diameter is 7.2 mm … Wikipedia
List of Tesla patents — Below is a list of Tesla patents. Dr. Nikola Tesla was an inventor who obtained around 300 patents [Snezana Sarbo, [http://www.tesla symp06.org/papers/Tesla Symp06 Sarboh.pdfNikola Tesla s Patents] , Sixth International Symposium Nikola Tesla,… … Wikipedia
History of electromagnetism — The history of electromagnetism, that is the human understanding and recorded use of electromagnetic forces, dates back over two thousand years ago, see Timeline of electromagnetism. The ancients must have been acquainted with the effects of… … Wikipedia
electromagnetism — /i lek troh mag ni tiz euhm/, n. 1. the phenomena associated with electric and magnetic fields and their interactions with each other and with electric charges and currents. 2. Also, electromagnetics. the science that deals with these phenomena.… … Universalium
Knob and tube wiring — (sometimes abbreviated K T) was an early standardized method of electrical wiring in buildings, in common use in North America from about 1880 to the 1930s. [Terrell Croft and Wilford Summers (ed), American Electricans Handbook, Eleventh Edition … Wikipedia
